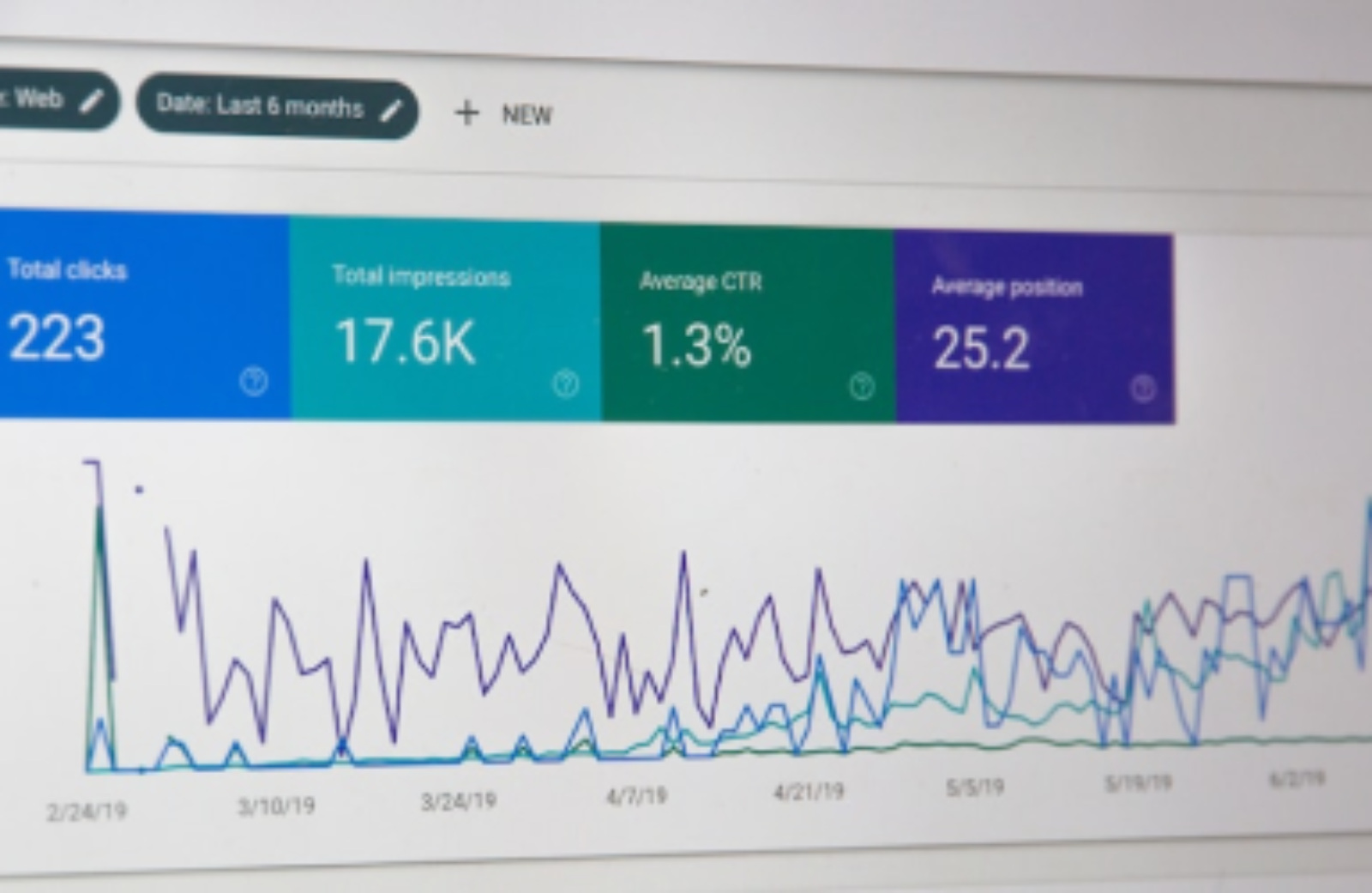
Let’s break down some key “SEO terms” and what they actually mean.
Let’s break down some key “SEO terms” and what they mean so you fully understand the concept and how it can help your business succeed.
Search Engine Optimization is the process of optimizing your website to increase its organic visibility in search engines such as Google. The higher a site ranks on Google or Bing, the more likely it will be clicked on by a user.
Sounds simple enough, right?
Well, there is a lot of work involved in getting to a higher rank, such as understanding SEO trends, building links to your website, creating content that people want to read, etc. But really, it’s an essential part of your business strategy – and when you get your head around it, it can be relatively easy to master. However, these are great things for your business because you are attracting more users, which means you can sell your products or services.
Even if you don’t want to do it yourself, understanding what it is and why it’s crucial means you can decide who does your SEO for you. So, let’s start at the beginning (it’s a perfect place to start) with some key terms and definitions that will help guide you through SEO.
What is SEO, and why does it matter??
SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization. It’s the process of setting up your webpage to show on search engines’ top results for searches of a specific phrase.
Let me break that down even further.
When it comes to SEO, there is you, the search engine (like Google and Bing), and the searcher. For example, if you have an article about “What we know of how google works?”. In that case, you want the search engine (usually Google) to show it as a top result to everyone who searches for the keyword “how google works.”
Search Engine Optimisation is the magic you’ve to work on to improve your website as one of the top results when people search for that term on Google. The easiest way to look at SEO as a whole is to split it into three elements:
Technical SEO
On-site SEO
Off-site SEO
These elements all work together to optimize your website. But it doesn’t have to be overwhelming. You don’t need to be an expert in every area of SEO to achieve great rankings — you just need to understand the basics and how to use them together.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO is the part of the process that involves ensuring that your website is coded correctly and running smoothly. To put it simply, technical SEO consists of all the steps you take on your website’s back-end to ensure that search engines can find and crawl your website. A few examples of technical SEO include:
Crawlability: Are your sitemaps accessible for search engines to crawl? The easier it’s for them to crawl, the easier it will be to find all your web pages and index them in their database.
Page speed: How quickly does your site load? A slow site can hurt user experience and your search rankings. Studies show that 40% of users abandon a website if it takes more than 3 seconds to load
Indexing: Search engines need to know what each page on your website is about to rank it accordingly. So, ensure that your content is accessible to search engines (i.e., no pages are blocked from search engines.)
Several free analysis platforms can test your website speed and recommend areas for improvement. These include GTmetrix, PageSpeed Insights, and Pingdom Website Speed Test.
Technical SEO isn’t always as sexy as keyword research or link building. However, it’s still an essential part of the process. After all, there’s no point in doing any other aspects of SEO if Google can’t crawl and index your site correctly!
On-Page SEO
On-Page or On-Site SEO is after the technical work has been done, you will need to optimize your website’s content. The goal is to make the site accessible for the search engines to crawl and understand the content. Your website will not rank well in search results if it doesn’t.
Content optimization starts with keyword research. You’ll want to find keywords with a good search volume or people searching for them. And they should be related to your business, products, or services.
Once you’ve got your keyword list, it’s time to focus on optimizing the elements of your site. ON-SITE SEO also covers simple site navigation, consistency in publishing content and using the best SEO keywords. Including spreading keywords naturally throughout the copy of your content. Optimizing meta tags, titles, descriptions, URLs, images and alt text, etc.
On-Page SEO is so important because it helps search engines understand what your website is about. This will help you rank for the right keywords and, ultimately, the correct type of traffic.
If you don’t do any On-Page optimization. In that case, you won’t be able to rank for any keyword related to your website!
Off-page SEO
Off-page SEO (also called “off-site SEO”) refers to actions taken outside your own website to impact your rankings within SERPs. These factors include link building (getting other websites to link to yours) and social media marketing.
Link building is a vast topic that we won’t be able to cover in this post. But we need to highlight why it’s so essential: search engines use links to crawl the Web. Think of it this way: the number of quality links a website has acted as votes of confidence from other websites. These votes tell search engines that your website is worthy of citation. In other words, off-page SEO is about getting other websites to talk about your business.
Off-site SEO factors are as vital as any of these SEO factors. If you have got this far and ignored off-page SEO factors, your efforts may come to nothing. It is that important. We attempt to convince search engines our content is valuable, credible, and trustworthy in our off-page SEO.
We do this by getting the website in front of people who will link to it. This could be through social media promotion or by commenting on blogs and forums (yes, they still exist). We can also target other websites that offer a related service or product that we do not provide. You can see how this would work if you were a pet shop with lots of knowledge about dogs, for instance, but did not sell dog food. An excellent place to earn links is on a dog food site.
Key SEO terms you need to know.
There are so many different SEO terms that it can be challenging to keep up with. Here’s a list of some key “SEO terms” to make things a little easier and what they actually mean so that you can better understand the concept.
SERP
When users type in a keyword or question, they get a list of results back from Google (or another search engine). That result page is called the “Search Engine Results Page,” or SERP. It includes organic search results (based on the page’s relevance to the user’s query) and paid ads.
Search intent
The term “search intent” or “user intent” is used to describe the purpose of an online search. It’s the reason a user inputs their query into a search engine, and it’s closely linked to what they expect to see in the results. Understanding search intent can help you target the right keywords and optimize your page for the best results. Most of these queries are part of the user journey online, but they often represent different stages.
Keywords
The words or phrases that describe the content of a webpage are given by users on Google or the Bing search box. They’re also used for PPC advertising and pay-per-click advertising. For example, you may have heard phrases like “long-tail keywords” or “keyword research.”
Long-tail keywords
Typically reflect niche groups and specific interests. These are more specific phrases that users are more likely to use near the end of the buying cycle. They tend to have smaller search volumes but convert much higher since their intent is more specific.
Organic traffic
These are visitors who find your website through unpaid search engine results. It’s the opposite of paid traffic, which comes from pay-per-click advertising (PPC) or other types of paid promotion.
Header Tags
Another way to think about header tags is to envision a piece of text broken up into sections or chapters. In this case, the header tag would be the title of each section and sub-section. The header tags are used to organize and define the structure of the content on your site.
Meta Description
A brief description (usually 160 characters or less) summarizes a webpage’s content. It shows up frequently in SERPs underneath your highlighted blue title tag.
Alt-text
Alt-text also called “alt attribute,” is a text that describes an image on a web page. It is written into the HTML code using the alt attribute and provides a text equivalent for a photo. It’s also vital for accessibility purposes as well as SEO.
Sitemap
A sitemap is an XML file that lists URLs to inform search engines which pages you consider important. The sitemap also contains metadata about each URL. Data like the last time it was updated, how frequently it usually changes, and how important it is linked to other URLs on the site. Learn how to submit your sitemaps here.
Uniform Resource Locator or URL
URL or Uniform Resource Locator is nothing more than the address of a specified unique resource on the Web. In principle, each valid URL links to a terrific resource. Such resources may be an HTML page, a CSS document, a picture, etc.
Plugin
They work like apps and add functionality to your site. It’s a separate program from the core WordPress software and typically specific to a particular function, like adding security or making it easier for users to share content on social networks.
Bounce rate
The percentage of users who leave a site after viewing only one page. A high bounce rate can indicate that the page doesn’t offer what users want.
Why is SEO so important for Google?
More sales, more brand awareness, and a better business. You can achieve all this by:
- Increasing your online visibility by ranking on Google and other search engines (so people can find you)
- Getting more users to click on your results (they might be interested in what you have to say)
- Keep those visitors on your site for longer (because they like what they see).
If you have a website and want to get more traffic, it should be part of your marketing efforts. Period. There are several ways to do marketing: You can advertise and promote on Facebook, Instagram, and Youtube. Still, SEO is one of the most effective ways to increase targeted traffic to your website.
It’s also cost-effective: As soon as you start your SEO marketing, you will reap the rewards of free, organic traffic. SEO helps small businesses compete with big companies: A well-optimized site can help small enterprises to outrank much larger ones with more significant resources
When people type into the Google search box for information related to your business, you want to show up. Ideally, you want to show up prominently. Research also shows that 60 percent of traffic from Google searches goes to websites that appear in the first three search results.
How can you get started with SEO Marketing?
Content marketing is the best way to improve your search engine rankings. No matter how much you spend on paid advertising, it’s still challenging to beat high-quality content.
Influencing search engines (SEO) takes time, but it pays off when you start reaching a relevant audience. If you’re just starting out, it’s best to get specific with your focus.
Here’s a tip: don’t write about general buying topics. For SEO results, the most common phrase you’ll hear is “quality content.” Quality content has a unique, instantly recognizable value and relevance to the search being performed on Google. This doesn’t mean simply providing helpful information to users; it means giving valuable data to Google.
You can do this by focusing on frequently searched topics, conducting research on what your target audience (your potential customers) are searching for, and figuring out how your content answers those questions. Providing an answer in a simple, logical fashion; and choosing SEO keywords that are easily understood by readers.
Once you start generating the content, build some early authority by promoting it in your email newsletter and social media platforms. You’ll establish yourself as the go-to thought leader in the process
Latest SEO trends That are Taking Center Stage in 2022
The first question that comes to mind is whether the latest SEO trends and tactics can help dominate the SERPs and earn more revenue in 2022? The answer is no doubt yes.
There’s no doubt that search engine optimization tactics continue to evolve. While it’s true that there are some timeless principles of SEO, like creating stellar content and identifying assets that deserve links and mentions, many older tactics aren’t as effective in today’s landscape.
In fact, some downright outdated tactics, such as keyword stuffing, can negatively impact your rankings. As user behavior evolves and search engines like Google adapt in response, the goal for today’s SEO professional is adaptability. And understanding what went on in the last year and what SEO looks like in 2022.
Here are the top SEO trends that are taking center stage in 2022:
- Core Web Vitals optimization
2021 Google page experience update was arguably the most significant change for search in the previous several years. This algorithm update will span several user experiences signals, including the Core Web Vitals, which evaluate users’ overall experience with the web page.
Core Web Vitals look at three key metrics:
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): the time it takes the largest content asset on the page to load. This excludes any content above the fold, which allows LCP to focus on what is most impactful: the main content of your page. Google says this should occur within 2.5 or fewer seconds of when the page first starts loading.
First Input Delay (FID): how long does your site take to respond to a user’s first interaction with it? The metric aims to capture delays caused by JavaScript, which can block browsers’ main threads and delay interactions by clicking or tapping on buttons. For example, if they click a link or type in a field, Google says this should happen within 100 milliseconds.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): measures visual stability and aims to prevent unforeseen changes when users interact with the carrier. The company also says you want to keep this score under 0.1, which means no more than one or two layout shifts occur on your page.
Of all the areas to direct your SEO investments in 2022, improving Core Web Vitals signals across your pages will have the most tangible impact on your search engine performance.
What you can do to optimize your page:
The key to success here is that you don’t need to reinvent the wheel — just optimize it. Small changes can make a significant impact. For example, moving CSS “above the fold” can improve LCP scores by 10 points. Optimize images by compressing them or improve server response times by upgrading hosting or reducing the number of plugins you use.
Find a tool that makes this easy: Core Web Vitals are complex, making them difficult to monitor and track on your own. You can recalibrate the performance of your page by checking with Google Search Console, PageSpeed Insights, and Chrome User Experience Report.
An SEO tool provides an automated way for you to assess how well each page meets these new metrics. Plus, they give you specific recommendations on what aspects of the page you should change to boost your performance score.
You might also focus on usability and user experience (UX) when designing your website (if applicable). Ensure your web pages are secure with HTTPS. Check out this details article on migrating from the default HTTP to HTTPS. - More Focus on Mobile User Experience
Jori Ford, Chief Marketing Officer at Food Boss, expects changes related to the mobile page experience. “Last March 2021, Google rolled out new tools to support mobile and page experience,” she explains.
Ford added, “With those pieces maturing, I think mobile page experience related to core web vitals as content will lead the charge.”
As SEO professionals, we tend to look at pieces, she said. “However, based on the recent tools, resources, and analytics updates, it’s apparent that the entirety of the mobile experience. From the discovery to how easily users interact, engage, and utilize, will come together just as content experience has over the last several years.”
A great way to improve your site’s mobile experience is to implement responsive web design (RWD) if you haven’t already. And improve page load speed by optimizing images and videos, minimizing redirects, and enabling browser caching and cookies.
“This will impact mobile UX and Core Web Vitals on mobile, mobile usability, mobile-first indexing, and mobile security,” she said. - Voice Search Will Impact Search Queries
If you’re not optimizing your content and website for voice search, you could be missing out on a massive chunk of the market. Thanks to innovations like Apple’s Siri, Google Assistant, and Amazon’s Alexa, voice search technology has exploded in recent years. As technology has gotten better, it’s also gotten more popular. In fact, statistic shows around 55 percent of U.S households will own a smart speaker in 2022, from 28 percent in 2018. That share is also projected to reach about 75 percent by 2025.
But what does this mean for businesses?
Voice queries are different from traditional web searches because they rely much more on natural language. Because people tend to use long-tail keyword phrases when they do voice searches and tend to abbreviate when typing. For example, a person might voice search, “What are the latest SEO trends for 2022?” but type “SEO trends 2022.”
This can be difficult for businesses to rank for them if they don’t have an SEO strategy focusing specifically on these keywords. To optimize your content for voice search, consider your keywords. You need to identify these longer phrases and incorporate them into your content marketing strategy. - AI will have a more significant impact on SEO
It’s fascinating to consider what life will be like in 10 years, or even half a decade. For those who have been around long enough, we remember what life was like when the Internet came into mainstream consciousness. Yet, today, it’s all but impossible to imagine our lives without it.
In many ways, artificial intelligence (AI) is where we were with the Internet back then — on the cusp of things that will change our world as we know it. And just as the Internet transformed how we interact with content online; AI will also begin to play a critical role in SEO strategy. Especially noteworthy is Google’s AI algorithm RankBrain. This will likely become one of the most important ranking factors for Google’s search engine results pages (SERPs). Since Google revealed RankBrain, many businesses have wondered how this will affect SEO. And how they can cater content strategy to an AI algorithm?
Though Google has not shared details on the inner workings of how RankBrain learns and analyzes content. Whizzes believe that user experience is one of its primary ranking factors. This means that the click-through rate and the number of time users spend on a website will be critical factors that RankBrain. - Supplement with Multimedia
One of the hottest trends in SEO today is multimedia. It’s something that every brand should be thinking about. Whether you’re building an internal video editor team or relying on a third-party vendor to create multimedia content for you.
We’ve noticed that people are wary of clickbait headlines and carefully constructed content these days. So, when you put your brand behind a piece of long-form content, you need to supplement it with multimedia. Also, it’s now easier than ever to put together some quick graphics with a tool like Canva or Venngage.
This means more than just slapping some stock photos in there. You want to test out multimedia elements like video, screenshots, or an infographic, making a comeback as people look for more ways to interact with the content they consume. You can also get creative by adding embedded tweets, animated GIFs, or creating a printable PDF guide or resource list that your readers can download! - Write Better Content That Fulfills Google’s EAT Principle
Today, the need for quality information on the web has never been greater. Users expect to find accurate data and trustworthy sources to navigate their daily lives, solve professional challenges, or make important decisions about their health. As a result, Google has reiterated the importance of content quality in determining search rankings. But just what does ‘quality’ mean to Google?
One way to look at this is through the EAT principle. E-A-T stands for Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. The concept was first introduced in 2014 but has taken on new significance after the infamous Medic Update in August 2018, when Google confirmed that this is something they use to evaluate websites.
These factors help determine if a page has valuable quality content. The concept of EAT is especially relevant in business niches under the YMYL. A quality rating for content that stands for “Your Money or Your Life” label includes industries like healthcare, finance, and law.
Google uses this acronym to classify pages that can potentially impact a person’s future happiness, health, financial stability, or safety. “YMYL websites” are held to the highest possible ‘EAT’ standards due to the subject matter and its meaning for users if that information is misrepresented.
How do we craft SEO content?
Well, here are a few tips for answering that question:
There are several ways you can ensure quality content. Start by creating buyer personas, which allow you to understand what kind of content will be most valuable to your audience. Next, understand the searcher’s intent which helps you map out the consumer journey to create the right content at each stage of their buying journey. Third, use this information from the buyer personas and search intent research to create content that fits the format that your users prefer. For example, video is probably preferable if you’re catering to teens. If you’re catering to an older audience, a video may be less appealing.
Finally, keep EAT in mind as you create your content:
Do you have the expertise to write about the topic? If not, can you find someone who does? Authority and trustworthiness are essential for SEO success in 2022. Can consumers trust what you say? This is where fact-checking and third-party data come in handy. Are there other experts who can confirm and build on your expertise? This is where co-authoring comes in handy and backs claims with statistics and facts. Link to reputable sites, such as “.gov” and “.edu” URLs. Having authoritative sites link back to you is another way to prove that you fulfill the EAT criteria. - A Shift to Long-Form Content
To ensure that you captivate and engage readers who visit your website, you will need to shift to a long-form content strategy. Long-form content of 2,000 words or more has been shown to get more traffic and shares than short-form content. Shifting your focus to creating quality long-form content can significantly improve your search rankings. However, for long-form content to be successful, it must be able to keep readers engaged.
To keep readers engaged, you must break up your content into multiple sub-sections using H2 and H3 subheadings, as this will make it more scannable. The goal is to make your content easy for readers to browse. Especially on mobile devices, big chunks of text can intimidate many readers and overwhelm a small screen. You should also make sure that your content is easy to share to improve SEO. Include obvious sharing links at the beginning and end of your content so that readers can share it with a click of a button. - Better Rich Snippets
The Internet is a vast and diverse place. Search engines use many techniques to enable users to find relevant content, including crawling through links, identifying keywords, and tracking user behavior. But all that information is only useful if the search engine knows what it means.
Google uses Schema markup as a microdata vocabulary to better understand and extract content from your pages. Schema enables Google to display more visually appealing results, called rich snippets. These rich snippets are designed to give users a better sense of what they’re likely to find when they click on the link, which increases the likelihood that they’ll click on it in the first place.
But you can tell Google how your site is organized by leveraging structured data markup. What types of content your site contains, such as video schema and education sites. This can also help Google understand which sections of your site are most essential and display those sections in search results.
Businesses that leverage schema markup is already far ahead of their competitors, as many digital companies still don’t utilize it. Take a look at Google’s complete list of rich results to see which are relevant to the content on your website. Also, make it a goal to add the appropriate schema markup in 2022.
The best SEO trends strategies for 2022
Overall, site owners and digital marketers should understand the key “SEO terms” and how google works this year. But do pay attention to tools and technology that might help your team save time and deliver more significant outcomes.
With so many SEO trends, it really becomes hard to keep up. But search engine optimization should be your top priority for ranking your website high. In fact, when compared with social media marketing, email marketing, and mobile optimization, SEO is a no-brainer. So, what are you waiting for? Get started with the best SEO trend(s) this year!
What Do We Know about how Google works? (So Far)
Businesses usually have a lot of questions about how Google works. How can Google set my company apart from the competition? Or You want to get your site ranking in the SERPs (search engine results pages), but you might not know where to start. And as you know, Google makes changes constantly—so it can be hard to predict what will work today and what won’t work tomorrow.
Luckily, we’ve put together a helpful guide on what we know about how Google works. This is an excellent place to start if you’re just getting started with your digital marketing strategy or looking for some new ideas to test out on your site. Read on!
What is Google?
Google is the world’s biggest search engine, with over 1.9 billion active users every month, and it’s a massive part of how we live. Most of us interact with Google daily, and it has become an essential part of our lives. Google is owned by Alphabet Inc., which also owns YouTube, Android, and several other businesses.
Google works by using an algorithm to find keywords that match the search query and rank them by relevance. The search engine will then display results based on how many times those keywords appear in each website’s content.
The company has a reputation for being an unlimited source of information. But you can turn Google inside out, and you’ll still only see the tip of the iceberg.
Google is an algorithm, not a human brain. It makes decisions based on the information it has available to it — and that information is made available by people, just like you and me.
Many factors behind how Google works, but links are the magic ingredient in how Google reads web pages. If your page gets a link from another website. In that case, that’s a signal to Google that it’s authoritative and worth ranking high in search results.
How does Google work?
Google’s search engine does not see the Internet the same way we do. It does not know a website or a page; it sees an index. An index is like a library catalog. A librarian may have one million books in their library, but they don’t hold them in their brains. They have a record that contains all of the information about each book, and they use that catalog to find the books when they need them.
Google has a specific algorithm that crawls the web and decides which pages are shown in which order. The index is stored in data centers worldwide, making Google so fast. When you type something into Google, it looks at its index to find the best results for your search query.
The first part of Google’s algorithm is called a “crawler.” The crawler tracks link from page to page, finding content on each page and adding it to its index. The second part of Google’s algorithm is called “PageRank,” which determines where each piece of content should appear in Google’s search results. PageRank evaluates more than 200 signals to rank pages and determine where they should appear in Google’s search results.
Google’s results page
Google has long been the most popular search engine, and its results pages are known as SERPs. Each page displays up to 10 site links, with the first few results often getting substantial clicks. The problem is that competition for these positions is fierce.
Most of the time, there are several paid links above the links on the first page. These links are advertising; people have paid Google to place these links at the top of the website when visitors search for a particular phrase. Prices for these ads vary substantially, depending on the search term’s competitiveness. There are also some other components that you can find on Google’s search engine results page and these organic and paid results.
Google’s results pages are highly customizable and personal. If you are logged in to your Google account and searching, you’ll see personalized results even if you’re searching anonymously. You may also see different results based on your physical location or browser settings (such as language preferences).
How Does Google Use Links?
Links are the magic ingredient when it comes to an understanding of how Google works. The more popular a page is, the more links it will have, and the higher up in the search results it will appear.
It’s not just about popularity, though. If you’ve ever been shopping for a new apartment and found yourself on StreetEasy. In that case, you know that sites like these often rank highly because they’re so comprehensive. Their job is to list every apartment in New York City, but that means they have a lot of pages with links all over them.
Let’s say you’re looking for an apartment in Brooklyn. A good search engine will know where you are (or at least what city you’re in) and give you different results than if you were searching from Los Angeles. It should also show you apartments for rent in Brooklyn before showing you apartments for sale there. In short, it needs to understand natural language and get smarter with every question asked of it.
Links are still important for other reasons. They help Google understand what it should rank for and what a page is about. They actually lead to active link building quite quickly. As long as you collect valuable and logical links, link building can be a good SEO strategy. But if you contain (or worse, buy) shady links, Google may punish you for that. Check out this article that discusses 5 link-building DON’Ts you didn’t know about.
How SEO and Google can Work for Your Business
If you’ve started looking into online advertising, you’ve probably heard about the value of using Google in your marketing. While strategies like direct marketing through pay-per-click (PPC) advertising or search engine optimization (SEO) can do a lot to boost lead generation for your business, it’s also important to consider how Google works.
This book by Eric Schmidt, Google’s former CEO, and Jonathan Rosenberg, an adviser to the current CEO Larry Page, is a carefully designed PR exercise. The authors point out that How Google Works is not about the technical functioning but how the company operates. The promise is that if you, too, manage a business (or desire to do so), you will learn the secrets of Google’s success. So, it would be best if you engaged “smart creatives.”
Many people would have you think there’s some magic involved, but the truth is pretty straightforward. But if there’s one thing this explanation should show, it makes Google so successful. Google is a leader in search and advertising because the company keeps a very close eye on data (particularly user behavior). Then Providing its users with the best results for their needs.
This may not be glamorous, but in this day and age where more than two-thirds of Internet users look for information online three times or more per week, data-driven decision-making will win out every time.
Ultimately, it’s a pretty straightforward process. Read through your data, decide what you want to do with the information, do something (or don’t do something), and repeat the process. It might not be as fun as having employees ride collectivist desks into the sunset. Still, it’s much more likely to result in a happy, thriving company. And that’s what Google wants most of all, right?
The Book
The book is an easy and exciting read. However, I wouldn’t recommend it for its management advice but instead as an entertaining and thrilling history of Google. My takeaway from the book is that if you attempt to copy Google to become a “Google,” you are entirely on the wrong road.
What makes Google exceptional is that it is a corporation driven by technology and creators in a place where leadership thinking rules. Both Jonathan Rosenberg and Eric Schmidt were managers when they started at Google. Before making Google a success, they had to adjust and adapt their management styles to succeed as Google employees.
Becoming Google
Let’s say you want to become the next Google. You want to be the next $200 billion company and create thousands of new millionaires and billionaires. How do you do it?
I’m going to tell you how NOT to do it. Don’t copy Google. Look at what Microsoft did in the late ’90s. They copied every aspect of Google’s business, from the search engine to the paid search advertising model, and then spread it across their entire empire — MSN, Hotmail, etc.
Then come 2022, Google will do a better job with search results, and people will start using Google more, not just for search but also for email, maps, and documents.
Instead of copying the company, let’s look at how some giants in computer technology came about. If you compare Apple, Microsoft, AT&T, and Google, each firm:
They ventured to an area where no one else had gone before, believing that their product would serve humankind. The brand didn’t copy products, business models, or corporate culture from anybody else.
Had leadership who understood how to make the company develop on the fly, learning from failures and appreciating successes
They continued reinventing themselves. Staying around was not an option because of severe rivalry in the case of Apple, Microsoft, and Google or the danger of government break-up in the case of AT&T.
Google’s success is primarily due to its focus on user experience. The company aims to provide relevant information and services quickly and efficiently to users worldwide. Many of Google’s products incorporate this focus on user experience — which has led to the company’s dominance in the internet search space — while others are simply data services that make use of the company’s vast network of information.
Recommended Reading?
Do I recommend reading the book? Definitely. It provides excellent insights into what it took to make Google “Google.” Both Jonathan Rosenberg and Eric Schmidt came to Google early in life, when the company was much smaller. They were a part of turning it into one of the most potent companies ever created. They’re also very well-qualified to write this book, as Schmidt has served as CEO and Chairman of Google. At the same time, Rosenberg is currently Senior Vice President for Product Management at Google.
The book is divided into three sections: “Management,” “Strategy,” and “Execution.” Each team is then divided into smaller units that cover specific topics within each more significant area. The book’s layout is easy to follow, but you will probably want to jump around from topic to topic with little regard for the order if you are like me. You can do so without losing context or getting lost in what you are reading.
The more we understand how Google works, the better we can tailor our efforts to produce the best results possible. While this post isn’t meant to be an exhaustive list of everything Google’s algorithms are looking for.

With over 10+ years experience working for Australia’s leading brands, we share some of the wisdom and latest trends in Digital Marketing (SEO/SEM/Social media), Web Design and App development